
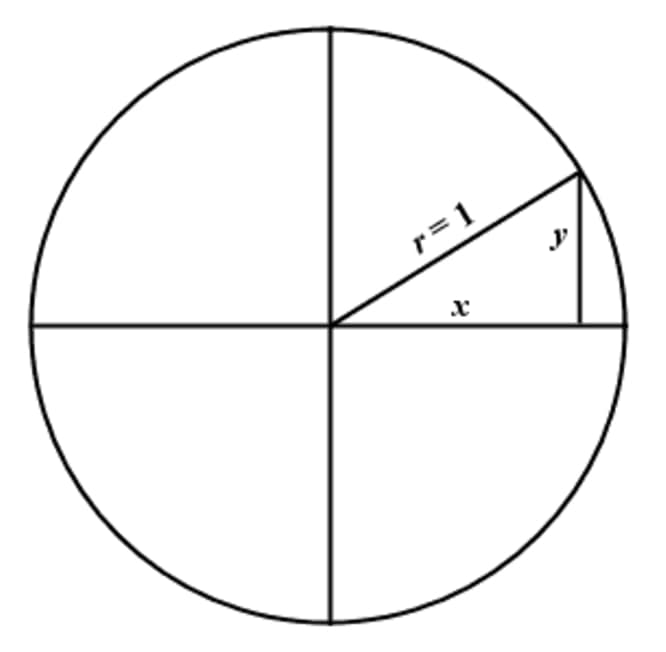
The area of the hexagon is 6 times the area of the triangle which is 3 3 / 2.
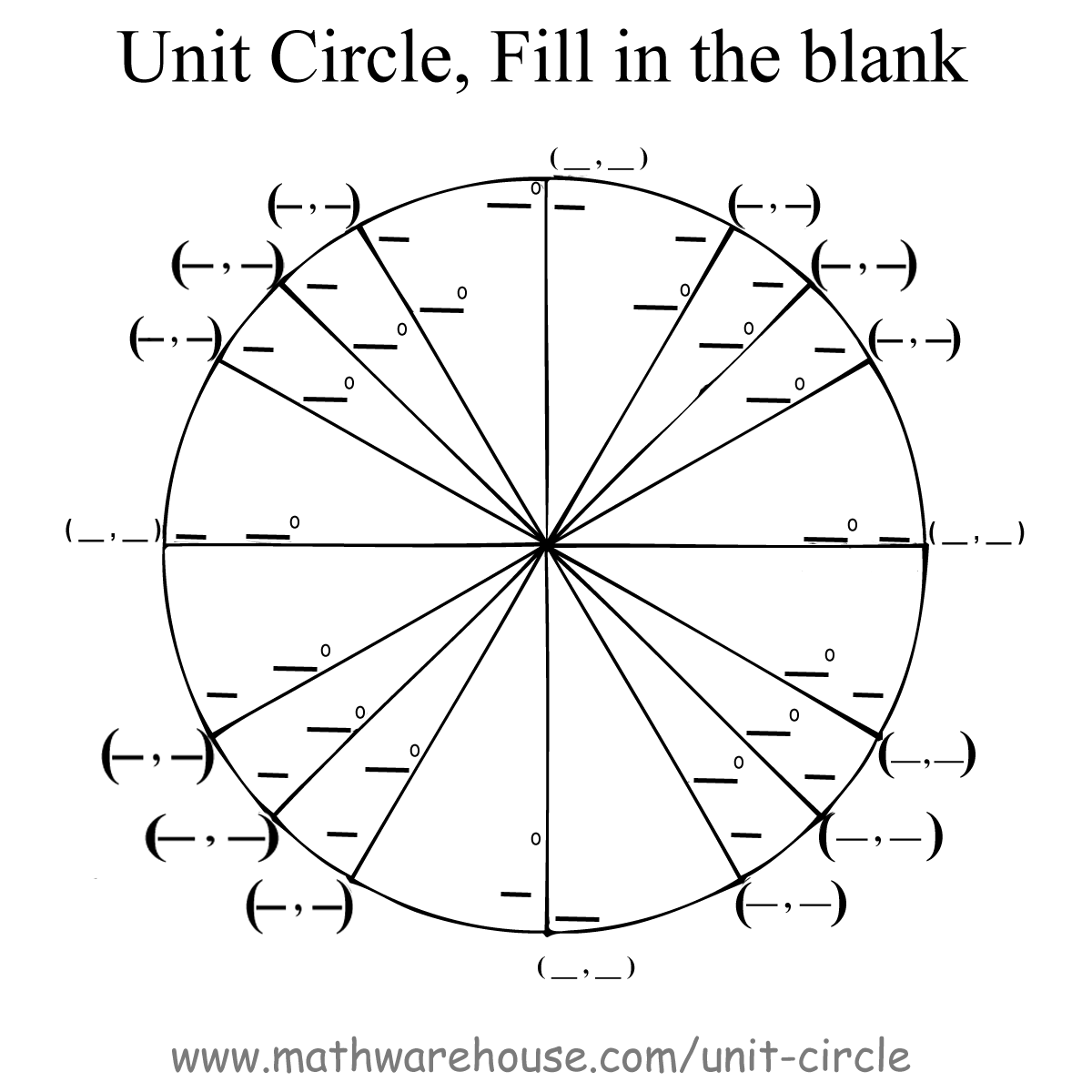
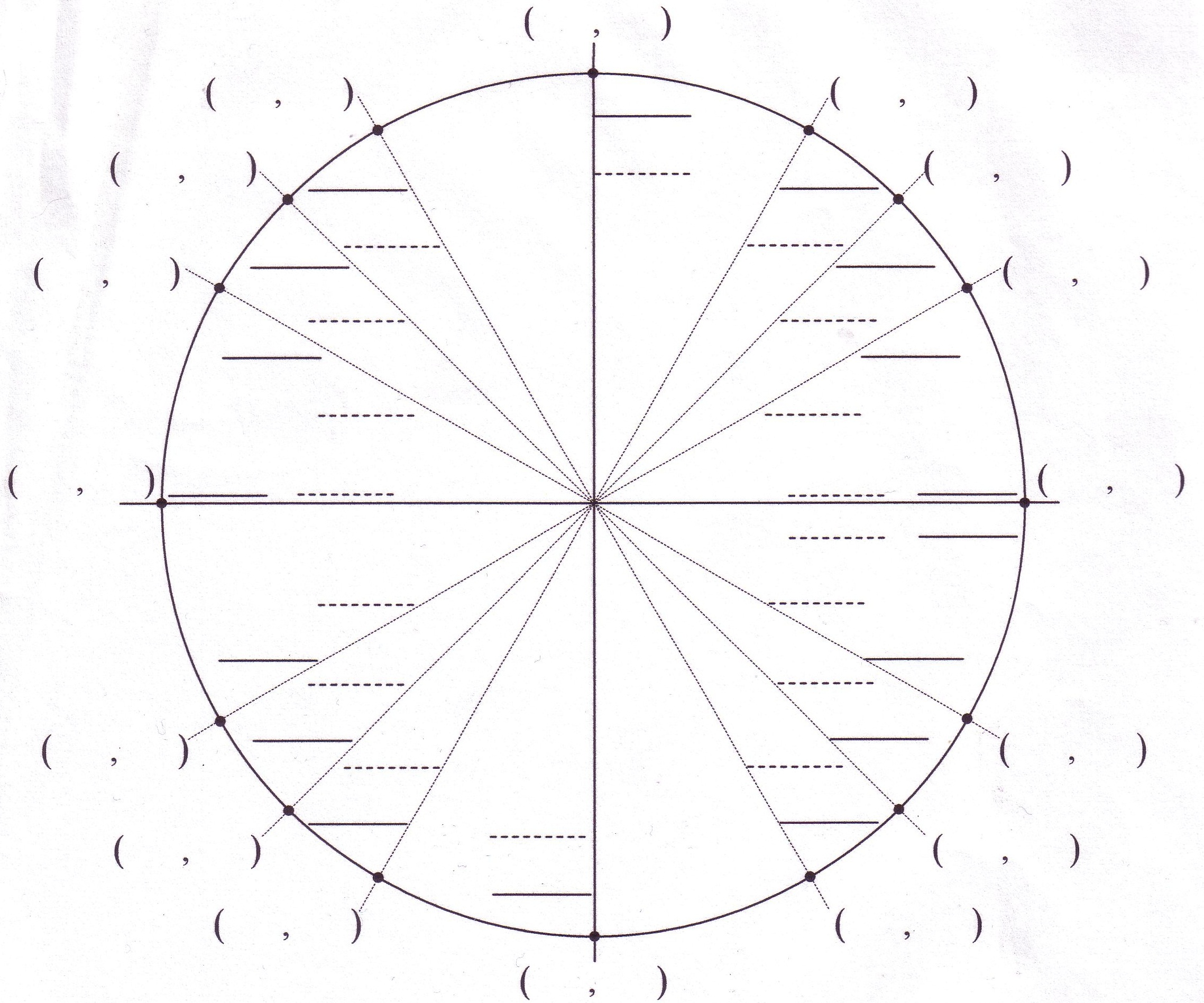
Visit Property Website All units Small Medium Large Amenities Units Availability 5x5 Self Storage Unit 25 Sq. So, for a hexagon, P H 2 6 tan 30 12 3 / 4 4 3 F 6: Area 1 2 a b sin C 1 2 ( 1) ( 1) sin ( 3) 3 / 4. CubeSmart Self Storage - 1406 Capital Circle NE, Tallahassee, FL Self Storage 25 - 400 Sq. We can define the trigonometry functions sine and cosine on the unit circle. f 6: For a unit circle, r 1, and so the perimeter of the regular polygon 2 n tan ( 180 n). Write the coordinates of each intersection point. It divides the circle into four quadrants (counter-clockwise) labeled as 1 st, 2 nd, 3 rd, 4 th quadrants, respectively. The following image illustrates which quadrant will have the positive or negative value of sine and cosine.įirst, we draw the two secants vertically and horizontally.
Iunit cirlce how to#
In this section, we will learn what is the unit circle, parts of the unit circle, and how to find the points of the unit circle. It is commonly used in the context of trigonometry. In brief, the unit circle denotes all the possible angles that exist with positive and negative values. A unit circle is a circle with radius 1 centered at the origin of the rectangular coordinate system. We can use it to explain all possible measures of angles from 0-degree to 360-degrees. It is used to explain the trigonometrical concept. And because the coordinate system involves circles and angles so much, trigonometric equations are vital to working in this system.In geometry, the unit circle is a special type of circle. There are a lot of interesting and cool to look at shapes that are much easier to define using polar coordinates. We happen to think the polar equation is much easier to work with in this case. Why might we want to use polar coordinates instead of our familiar Cartesian system? Compare the equations for the same circle, centered on the origin with radius 4: Instead of x and y, it defines a point using r, the radius, and θ (pronounced "theta"), for an angle.
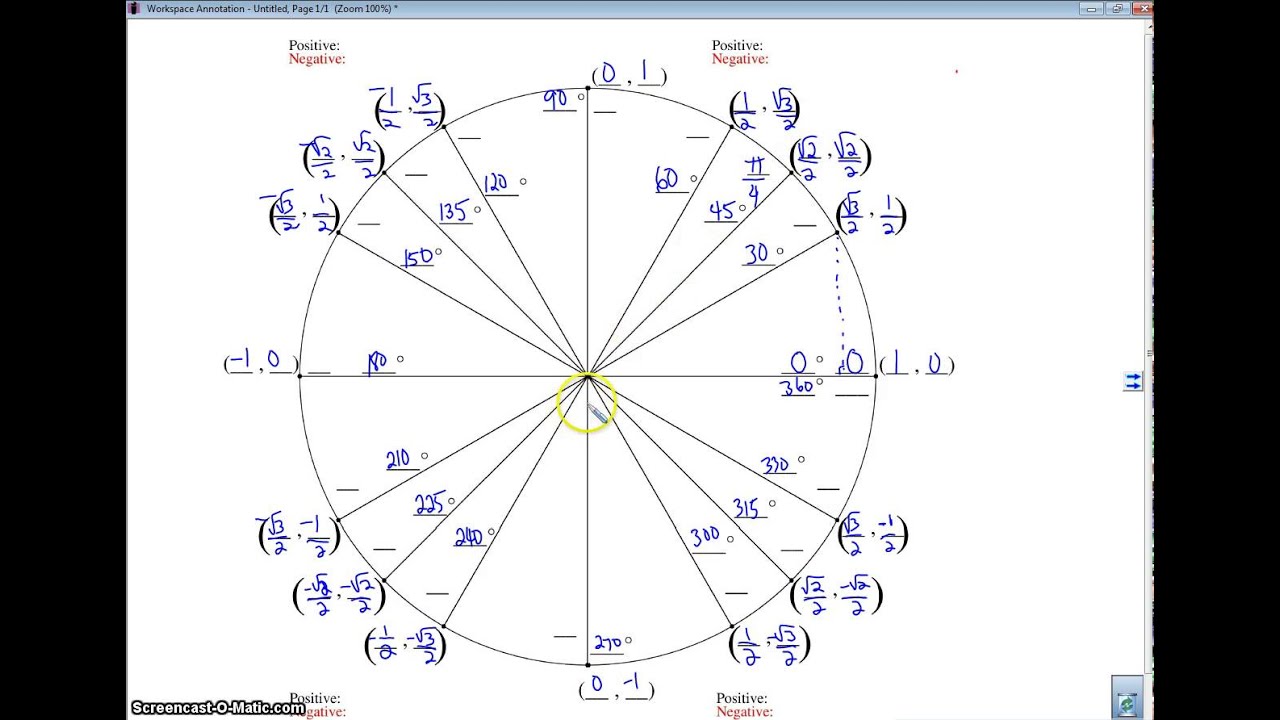
If it did, Teddy Roosevelt would come in and trust-bust it up one axis and across the other.Ī different kind of coordinate system is the polar coordinate system. The Cartesian system doesn't have a monopoly on graphing, though. They have two axes, x and y, and any point on the graph is defined by a coordinate with both an x and y component. BIG IDEA Every point P on the unit circle has coordinates of the form (cos, sin ), where is the magnitude of a rotation that maps (1, 0) onto P. The Cartesian coordinate system is a fancy name for the graphs we've always made.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
